N皇后问题(常见解法 Java实现)
N皇后问题也是算法题中的经典题目,也有很多种不同的解法。这里就实现并总结一下常见的解法。
背景简介
N皇后问题是国际西洋棋棋手马克斯·贝瑟尔于1848年提出:
在8×8格的国际象棋上摆放八个皇后,使其不能互相攻击,即任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上,问有多少种摆法。

主要是回溯思想的体现。
下面将介绍常见的N皇后四种做法,当然还有很多其他的做法。
递归求解
N皇后问题,在递归解法下,第一种自然的做法是采用二维数组来表示棋盘。
二维数组表示棋盘还是比较直观好理解的。
贴上代码:
1 | package com.chain.algorithm.test.day02; |
递归方法-二维数组方法的测试结果:
1 | queen: 4 |
分析代码可知,二维数组的情况下,在比较时的操作次数是非常惊人的,下面尝试使用一维数组来进行改进。
第二种做法,将二维数组改成一维数组。既降低了时间复杂度,也压缩了空间复杂度。
一维数组下标表示棋盘的行数,值表示该行的皇后放置的位置。
贴上代码:
1 | package com.chain.algorithm.test.day02; |
递归方法-一维数组方法的测试结果:
1 | queen: 4 |
由此可见,在递归方法下使用一维数组的话效率提升近一倍。
当然还有一种改进,就是用手动栈来代替系统栈,不过就单从效率上比较的话,和使用系统递归的做法相比不明显,不如直接使用循环。
循环求解
这里使用一维数组来记录值,将递归改造成循环。效率和递归相比,没有多少变化。
贴上代码:
1 | package com.chain.algorithm.test.day02; |
循环方法-一维数组方法的测试结果:
1 | queen: 4 |
位运算法
由于数据在计算机中是以二进制的形式存储的,因此位运算指令的执行速度是很快的。如果判断冲突时,能够使用位运算代替算术运算,可以取得较高的运行效率。
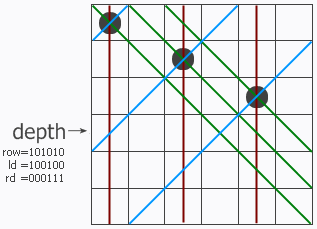
位运算采用递归做法,循环做法并不能带来明显的效率提升。
贴上代码:
1 | package com.chain.algorithm.test.day02; |
递归方法-位运算方法的测试结果:
1 | queen: 4 |
由此可见,使用位运算的速度提升是非常明显的,这也是目前比较快的做法。
在求解的结果中,可以发现有些是对称的,因此还可以进行进一步的剪枝,这里就不做研究了。
测试代码
最后再补充贴上测试代码:
1 | package com.chain.algorithm.test.day02; |